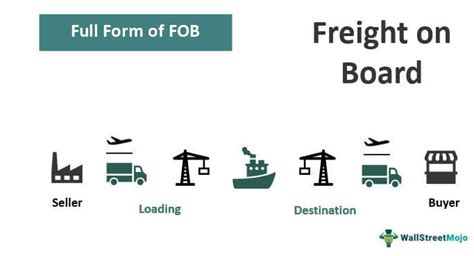
What Is Fob Charges
Fob charges, or Free on Board charges, are a critical component of international trade and shipping. They represent the costs and responsibilities associated with transporting goods from the seller's facility to a specified destination, typically an overseas port.
Understanding Fob charges is essential for businesses engaged in global commerce, as they impact the overall cost of doing business and can significantly influence a company's bottom line. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Fob charges, exploring their definition, how they work, their advantages and disadvantages, and their real-world implications.
The Definition of Fob Charges
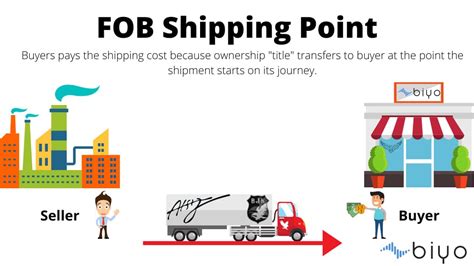
Fob charges are the expenses incurred when goods are shipped from the seller's premises to a designated location, often an international port. These charges cover the costs associated with loading the goods onto the transportation vessel, be it a ship, plane, or truck, and the subsequent transportation to the agreed-upon destination.
The term "Free on Board" originates from the idea that the seller is responsible for the goods until they are loaded onto the transportation vessel, after which the buyer assumes ownership and associated risks.
How Fob Charges Work
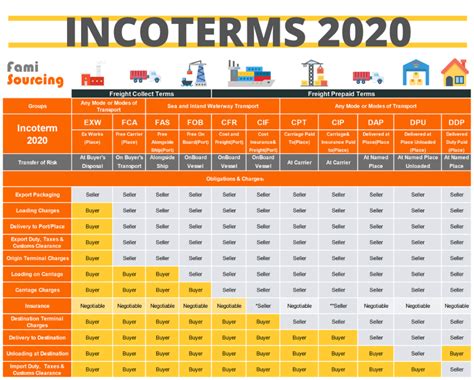
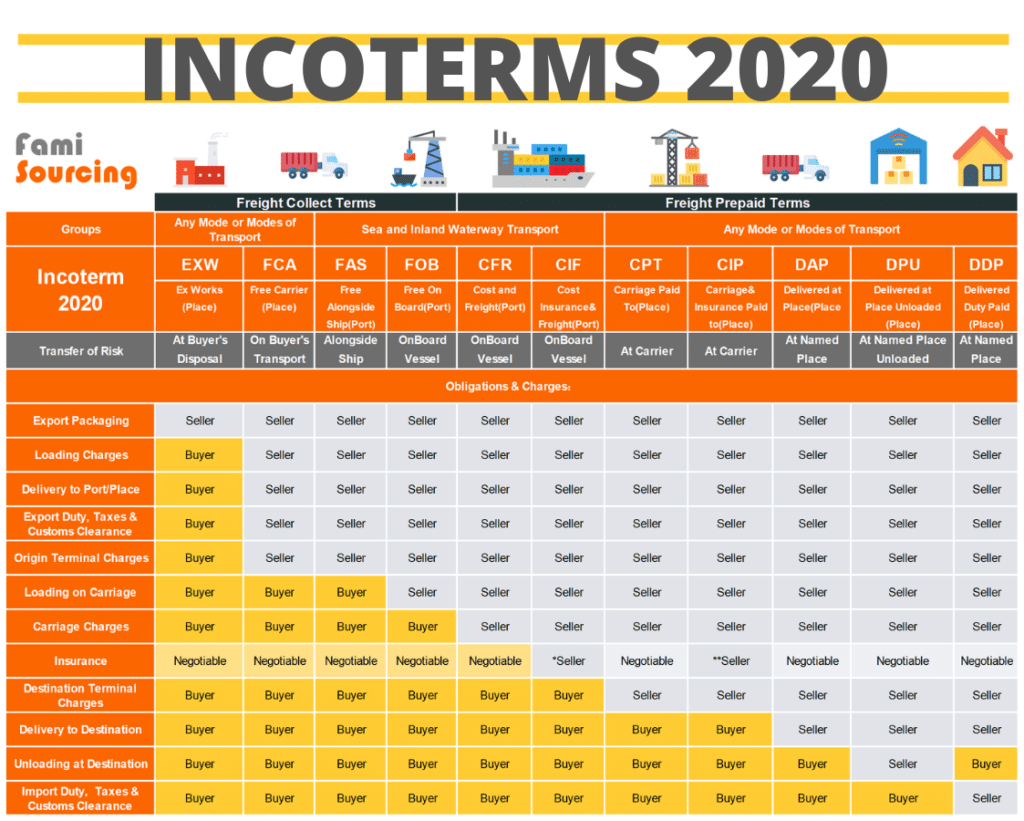
The Incoterms
Fob charges are governed by a set of international commercial terms known as Incoterms. Incoterms are a series of predefined rules and guidelines established by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) to facilitate global trade by providing clarity and standardization to international sales contracts.
The Incoterms outline the responsibilities and costs associated with the delivery of goods, including Fob charges. They define the point at which the seller's responsibilities end and the buyer's begin, which is crucial for determining liability in case of any issues during transit.
Key Elements of Fob Charges
Fob charges typically encompass the following elements:
- Loading Costs: These include the expenses associated with loading the goods onto the transportation vessel. This may involve labor costs, equipment rental, and any necessary infrastructure or services to facilitate the loading process.
- Transportation Fees: Fob charges cover the costs of transporting the goods from the seller's facility to the agreed-upon destination. This includes the actual shipping costs, which can vary based on the mode of transportation and the distance traveled.
- Documentation and Customs: Fob charges may also include the costs of preparing and processing the necessary documentation for international shipping. This includes bills of lading, commercial invoices, and any required customs declarations.
- Insurance: Depending on the Incoterms agreed upon, Fob charges might include insurance coverage for the goods during transit. This ensures that the buyer is protected against potential losses or damages during the shipping process.
Advantages of Fob Charges
Clarity and Risk Management
One of the key advantages of Fob charges is the clarity they provide in international trade. By clearly defining the responsibilities and costs associated with shipping, Fob charges reduce the potential for misunderstandings and disputes between buyers and sellers.
With Fob charges, the buyer knows exactly what they are paying for and when their ownership and liability begin. This clarity helps in risk management, as both parties understand their roles and can plan accordingly.
Flexibility and Cost Control
Fob charges offer flexibility to both buyers and sellers. Buyers can choose their preferred shipping methods and routes, potentially reducing costs or optimizing delivery times. Sellers, on the other hand, can negotiate better shipping rates by leveraging their relationships with freight forwarders or shipping companies.
This flexibility allows businesses to adapt to changing market conditions and optimize their supply chain based on factors like cost, speed, or reliability.
Disadvantages of Fob Charges
Complexity and Administrative Burden
While Fob charges provide clarity, they can also introduce complexity, especially for businesses that are new to international trade. The need to understand and comply with Incoterms, prepare extensive documentation, and navigate the complexities of international shipping can be a significant administrative burden.
Additionally, the potential for errors or delays in documentation or customs clearance can further complicate the process and impact the overall efficiency of the supply chain.
Limited Control over Shipping Process
Under Fob charges, the seller’s control over the shipping process ends once the goods are loaded onto the transportation vessel. While this shift in responsibility is intended to reduce the seller’s liability, it can also mean that the seller has limited control over the subsequent handling and transportation of the goods.
This can be a concern for businesses that require a high level of control over their supply chain, as they may not have the same level of visibility or influence over the shipping process once the goods are in transit.
Real-World Implications
Case Study: Global Retailer’s Supply Chain
Consider a global retailer that sources products from manufacturers in Asia. The retailer opts for Fob charges when shipping goods from the manufacturer’s facility to their distribution centers worldwide.
Under Fob charges, the manufacturer is responsible for loading the goods onto the transportation vessel and ensuring they are properly documented and insured. Once the goods are loaded, the retailer assumes ownership and takes on the associated risks and costs of transportation.
This arrangement allows the retailer to benefit from the manufacturer's established shipping relationships and expertise. It also provides the retailer with flexibility in choosing shipping routes and methods to optimize their supply chain based on factors like cost, speed, or environmental impact.
Impact on Small Businesses
For small businesses entering the world of international trade, Fob charges can present both opportunities and challenges. On the one hand, Fob charges provide a clear framework for understanding and managing the costs and risks associated with shipping.
However, the administrative burden and potential complexity of Fob charges can be daunting for smaller businesses with limited resources. They may require additional support or expertise to navigate the intricacies of international shipping and ensure compliance with Incoterms and customs regulations.
Future Implications and Trends
Digitalization and Automation
The rise of digital technologies and automation is transforming the way Fob charges are calculated and managed. Advanced logistics software and platforms are making it easier for businesses to track and manage their supply chains, including the costs associated with Fob charges.
These technologies can automate the generation of shipping documents, provide real-time visibility into the shipping process, and even offer predictive analytics to optimize shipping routes and reduce costs.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
With growing concerns about the environmental impact of global shipping, Fob charges are also evolving to incorporate sustainability considerations. Businesses are increasingly looking for ways to reduce their carbon footprint and minimize the environmental impact of their supply chains.
This may involve choosing shipping methods with lower carbon emissions, optimizing routes to reduce fuel consumption, or investing in more sustainable packaging and shipping materials. Fob charges will need to adapt to incorporate these sustainability goals while still providing businesses with the flexibility and control they require.
Globalization and Emerging Markets
As global trade continues to expand and new markets emerge, Fob charges will play a crucial role in facilitating international commerce. The development of infrastructure and shipping capabilities in emerging markets will impact the cost and efficiency of Fob charges, opening up new opportunities for businesses.
However, the increasing complexity of global supply chains and the potential for geopolitical risks will also pose challenges. Businesses will need to navigate these complexities while ensuring that their supply chains remain resilient and efficient.
How are Fob charges calculated?
+Fob charges are calculated based on the specific costs associated with loading and transporting goods from the seller’s facility to the agreed-upon destination. This includes loading costs, transportation fees, documentation expenses, and potentially insurance coverage. The exact calculation can vary based on the mode of transportation, distance traveled, and any additional services required.
What are the key Incoterms relevant to Fob charges?
+The Incoterms most commonly associated with Fob charges are FOB (Free on Board) and CFR (Cost and Freight). FOB Incoterms define the point at which the seller’s responsibilities end, typically when the goods are loaded onto the transportation vessel. CFR Incoterms, on the other hand, include both the cost of the goods and the freight charges up to the agreed-upon destination.
How do Fob charges impact small businesses entering international trade?
+Fob charges can provide small businesses with a clear framework for understanding and managing the costs and risks of international shipping. However, the administrative burden and complexity of Fob charges can be a challenge for smaller businesses. They may require additional support or expertise to navigate the intricacies of international shipping and ensure compliance with Incoterms and customs regulations.


