States Without Toll Roads
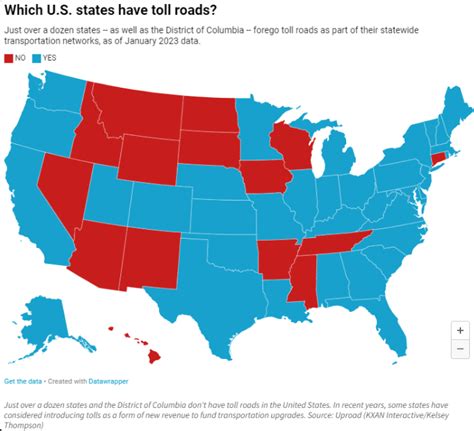
In the United States, the concept of toll roads has been a prevalent method of financing and maintaining highways and infrastructure for decades. However, not all states have embraced this model, and some regions have chosen to prioritize toll-free travel for their residents and visitors.
This article aims to delve into the fascinating world of states that have resisted the implementation of toll roads, exploring the reasons behind their decisions, the alternative funding mechanisms they employ, and the potential implications for transportation infrastructure and user experience.
The Case for Toll-Free States

Several states across the US have adopted a toll-free approach to their road networks, offering motorists uninterrupted journeys without the need for toll payments. This decision often stems from a combination of historical, cultural, and economic factors unique to each state.
One of the primary motivations behind avoiding toll roads is the desire to maintain equitable access to transportation. In states with diverse populations and varying economic backgrounds, the absence of toll fees ensures that all residents, regardless of their financial status, can travel freely without incurring additional costs.
Historical Context
The history of a state can significantly influence its stance on toll roads. Many states with a rich historical heritage, particularly those with strong agricultural or rural roots, have long advocated for free public roads as a symbol of connectivity and community. For instance, Nebraska, known for its vast plains and agricultural industry, has a long-standing tradition of toll-free travel, with the state’s first major highway, the Lincoln Highway, being constructed as a toll-free route in the early 20th century.
Public Opinion and Politics
Public sentiment towards toll roads plays a crucial role in a state’s decision-making process. States with strong citizen engagement and a preference for limited government intervention often view toll roads as an unnecessary burden. Political leaders, responsive to their constituents’ wishes, may opt to prioritize alternative funding methods to maintain roads and bridges.
| State | Notable Toll-Free Initiatives |
|---|---|
| Iowa | Iowa's resistance to toll roads dates back to the early 1900s, with a strong public stance against tolling major highways. |
| South Dakota | Despite facing infrastructure challenges, South Dakota has consistently rejected toll proposals, favoring user taxes and federal grants. |
| Vermont | Vermont, with its scenic landscapes, has a long history of toll-free travel, including the famous Appalachian Trail, which traverses the state. |

Alternative Funding Strategies

So, if these states eschew toll roads, how do they finance their vast road networks and infrastructure projects? States without toll roads employ a variety of innovative and traditional funding mechanisms to maintain their transportation systems.
Fuel Taxes and User Fees
One of the most common methods is the imposition of fuel taxes, where a percentage of the price paid at the pump goes towards road maintenance and construction. These taxes are often accompanied by vehicle registration fees and other user-based charges, ensuring that those who use the roads contribute to their upkeep.
| State | Fuel Tax Rate (per gallon) |
|---|---|
| Alaska | $0.30 |
| Wyoming | $0.34 |
| South Carolina | $0.16 |
General Fund Allocations
In some states, a portion of the general fund, derived from various taxes, is dedicated to transportation infrastructure. This approach ensures that road maintenance and improvements are considered essential public services, receiving consistent funding from the state’s overall budget.
Federal Grants and Aid
States without toll roads often rely heavily on federal assistance, such as grants and loans, to finance large-scale projects and address critical infrastructure needs. This collaboration between state and federal governments ensures that vital transportation networks remain functional and up-to-date.
Public-Private Partnerships
In recent years, several states have explored public-private partnerships (P3s) as a means to leverage private sector expertise and funding for infrastructure projects. These partnerships can involve various arrangements, such as design-build-finance contracts, where private entities contribute to the upfront costs of projects in exchange for long-term revenue streams.
Implications and Challenges
While the toll-free approach offers benefits like equitable access and a sense of community, it also presents unique challenges and considerations for states and their residents.
Funding Shortfalls
One of the primary concerns is the potential for funding shortfalls, especially in states with rapidly growing populations and expanding road networks. Without toll revenues, the burden of financing infrastructure falls solely on the state’s shoulders, which can be a significant challenge during economic downturns or when federal aid is limited.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Maintaining a vast road network without toll revenues requires efficient allocation of resources. States must prioritize repairs and upgrades based on traffic volume, safety concerns, and economic impact, often making difficult decisions to ensure that limited funds are utilized effectively.
Impact on Rural Areas
Toll-free states, particularly those with large rural populations, face the challenge of providing adequate transportation infrastructure in less densely populated areas. Ensuring that rural residents have access to well-maintained roads and reliable transportation can be a complex task, often requiring innovative funding solutions and strategic planning.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Toll-Free States
As the transportation landscape evolves, states without toll roads will need to adapt and innovate to meet the changing needs of their residents and the evolving demands of the industry.
Emerging Technologies
The integration of advanced technologies, such as autonomous vehicles and connected infrastructure, presents both opportunities and challenges for toll-free states. These technologies can improve safety and efficiency, but they also require significant investments in research, development, and infrastructure upgrades.
Sustainable Funding Models
States will need to explore sustainable and resilient funding models to ensure long-term financial stability for their transportation networks. This may involve a combination of traditional funding sources, such as fuel taxes, and innovative approaches, like road usage charging or vehicle miles traveled (VMT) fees, which directly link user fees to actual road usage.
Collaboration and Regional Planning
Regional collaboration and strategic planning can play a crucial role in the future of toll-free states. By working together, states can pool resources, share best practices, and develop comprehensive transportation plans that address regional connectivity and economic development needs.
Conclusion
The decision to avoid toll roads is a complex one, influenced by a state’s unique cultural, economic, and historical context. While toll-free states face funding and infrastructure challenges, their commitment to equitable access and community-centric transportation networks is commendable. As the transportation industry continues to evolve, these states will need to embrace innovation, collaboration, and sustainable funding strategies to ensure their road networks remain safe, efficient, and accessible for all.
Which US states have the highest number of toll roads?
+States like New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and California have extensive toll road networks, with multiple toll highways and bridges.
Are there any toll roads in Alaska or Hawaii?
+No, both Alaska and Hawaii are free of toll roads, primarily due to their unique geographic and economic circumstances.
How do toll-free states compare in terms of road quality and maintenance?
+Road quality and maintenance can vary across toll-free states, influenced by factors like funding, population density, and geographic challenges. Some states excel in maintaining their road networks, while others face challenges in allocating sufficient resources.


